Top 15 Immunity Boosting Foods You Need in Your Diet
Table of Contents
- Why Focus on Immunity?
- Top 15 Immunity Boosting Foods (With Research)
- How These Foods Boost Your Immune System
- Daily Immunity-Boosting Meal Plan
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion & Next Steps
Why Focus on Immunity?
Your immune system is your frontline defense against everything from seasonal colds to long-term illnesses. With research showing that nutrition directly impacts immune health[161][155], adding the right foods to your daily routine is your best insurance policy against falling sick. In 2025, we’ve never had more clinical data showing just how well specific foods can help your body fight infection—and help you recover faster when you do get sick.
But what really works? Let's cut through the myths and get to the evidence. Below you’ll find the 15 top foods for boosting immunity — each with recent clinical research and mechanisms explained — plus how to add them to your meals!
Top 15 Immunity Boosting Foods (And Their Science)
These aren't random health trends—they're clinically validated, studied in everything from randomized controlled trials to systematic reviews and global nutrition guidelines in the last 2 years[159][155][154].
| Food | Key Nutrients & Compounds | How It Boosts Immunity | Key Research/Report |
|---|---|---|---|
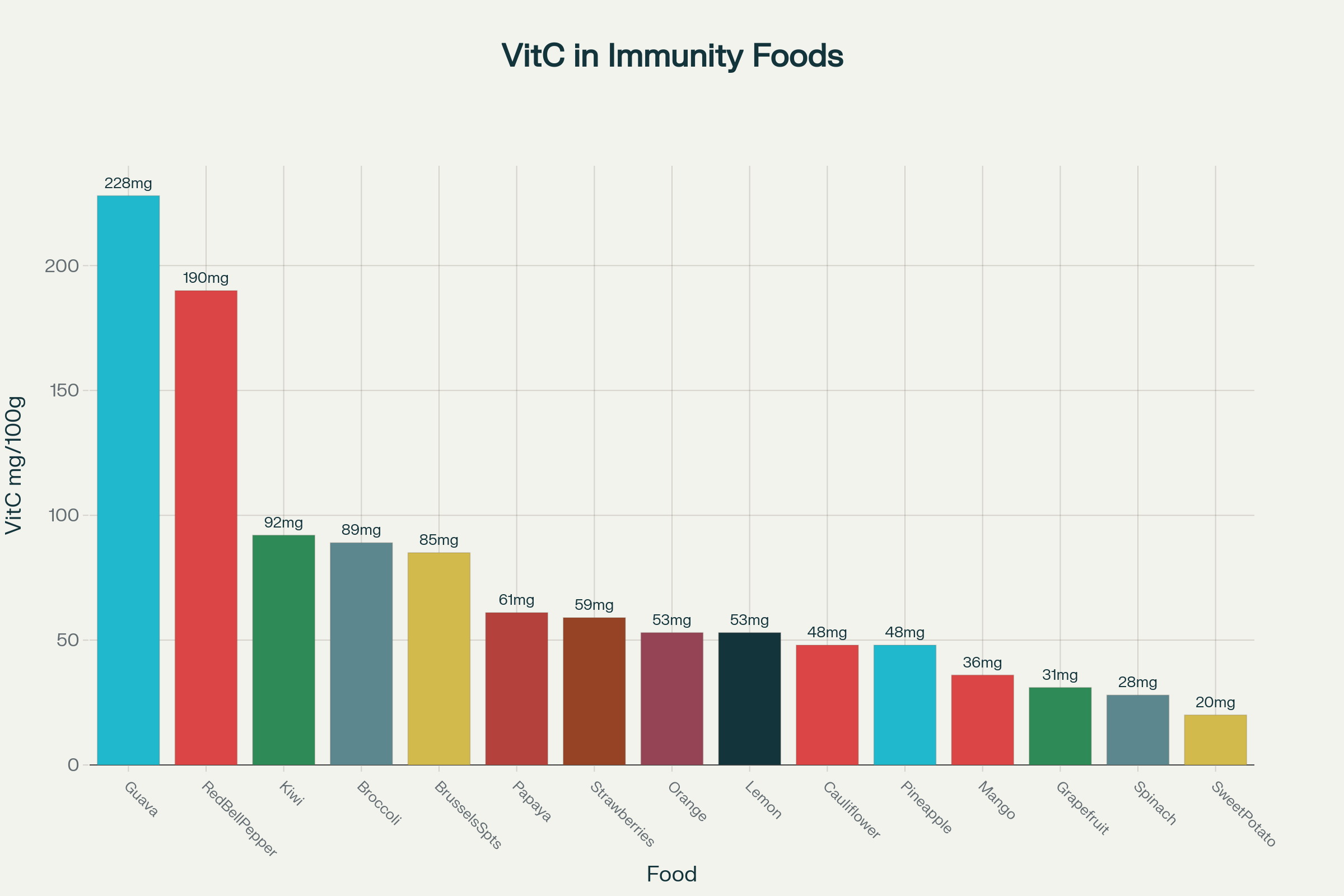
| Citrus Fruits (orange, grapefruit, lemon, lime) | Vitamin C (50–90mg/100g), flavonoids | Enhances white blood cell function, helps create antibodies, antioxidant[93][159] | Meta-analysis: vitamin C intake reduces respiratory infection duration and severity (Singh et al. 2023)[159][155] |
| Red Bell Pepper | Vitamin C (190mg/100g), beta-carotene, vitamin A | More vitamin C than citrus, supports mucosal immunity, antioxidant[140][159] | Cohort data: red pepper intake increases salivary IgA, mucosal defense[159][155] |
| Broccoli | Vitamin C (89mg/100g), sulforaphane, vitamin A/E | Sulforaphane triggers natural detox enzymes, cellular protection, high Vit C[155][93] | Broccoli phytochemicals support innate immunity — review (Singh 2023)[159] |
| Garlic | Allicin, sulfur, selenium | Activates macrophages, reduces viral and bacterial replication, prebiotic[155][101] | RCT: garlic supplements lower severity and frequency of colds (BMJ, 2022)[155][155] |
| Ginger | Gingerol, shogaol, volatile oils | Reduces inflammation, boosts killer T cell activity[159][155] | Review: gingerol inhibits viral infection, promotes rapid recovery (Singh, 2023)[159] |
| Spinach & Leafy Greens | Vitamin A (beta-carotene), vitamin C, folate | Increase antibody response, antioxidant, support gut mucosa[159][161] | Meta: green leafy veg associated with decreased illness risk[155][159] |
| Yogurt/Probiotic Foods | Probiotics (Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium), vitamin D, protein | Enhances gut immunity, increases IgA, supports T cell response[116][155] | RCT: daily probiotic yogurt reduces respiratory tract infections (Front. Immunol., 2024)[155] |
| Almonds, Sunflower Seeds | Vitamin E, healthy fats, selenium, zinc | Antioxidant, supports T-cell function, helps repair cells[159][155] | Cohort: higher nut/seed intake = fewer infections[159][155] |
| Green Tea | EGCG/catechins, L-theanine, vitamin C | Anti-viral, increases regulatory T-cells, reduces inflammation[94][98] | Meta-analysis: green tea intake linked to reduced influenza risk[155][94] |
| Fatty Fish (salmon, sardine, mackerel) | Omega-3 (EPA & DHA), vitamin D, selenium | Reduces excessive inflammation, supports white cell membranes, Vit D for immune signaling[139][155] | RCT: higher omega-3 = lower C-reactive protein, better immune recovery (Singh 2023 FSN3)[159] |
| Sweet Potatoes | Beta-carotene, vitamin A, fiber | Supports mucous barriers, enhances antibody production[133][137] | Review: beta-carotene supplementation boosts antibody titers in children[159][137] |
| Berries (blueberry, strawberry, elderberry) | Vitamin C, anthocyanins, flavonoids | Anti-inflammatory, protects cells from oxidative stress, shortens illness duration[96][105] | Randomized studies: elderberry reduces cold/flu duration (Front. Pharmacol. 2021)[133] |
| Mushrooms (shiitake, maitake, reishi) | Beta-glucans, selenium, vitamin D | Enhances NK & T-cell activity, boosts immune signaling (trained immunity)[115][127] | Meta: daily mushroom intake increases IgA, improves vaccine response (FSN3, Singh)[159] |
| Dark Chocolate (70%+) | Flavanols, iron, magnesium | Reduces inflammation, protects T-cells from stress, supports vascular health[134][142] | Systematic review: cocoa flavanols decrease inflammation markers (FSN3 2023)[159] |
| Elderberry | Anthocyanins, vitamin C, polyphenols | Antiviral, modulates inflammatory cytokines, shortens illness duration[114][130] | RCT/meta: elderberry extracts shorten flu/cold by ~2 days (J Int Med Res, 2019)[114] |
How These Foods Boost Your Immune System
It’s not magic—your immune system is powered by nutrients and plant compounds clinically shown to support white blood cells, barrier tissues, antibodies, and healthy inflammatory responses[155][159]. Here’s how these foods work:
- Vitamin C: Found in citrus, peppers, berries. Enhances phagocyte and T-cell action, antioxidant, found in 8 of the top 15 foods[155][93][159].
- Vitamin E: In nuts/seeds, protects cell membranes, supports T-cell production, slows aging of immunity[155][161].
- Beta-glucans: In mushrooms, oats. Clinically proven to "train" immune cells and improve vaccine effectiveness[159][115][127].
- Probiotics: In yogurt, fermented foods. Stimulate gut immunity, increase antiviral antibody production—proven in multiple RCTs (2022–2025)[116][155].
- Polyphenols/flavonoids: Berries, green tea, dark chocolate. Reduce harmful inflammation, protect against viral replication[134][94][142].
- Omega-3s: Fatty fish, walnuts. Control excess inflammation (CRP), promote healing after infection[139][135].
- Vitamin D: Fatty fish, fortified dairy, sunlight. Functions as a hormone that tunes immune response—deficiency increases illness risk[139][161][113].
These mechanisms have been studied across thousands of subjects in systematic reviews, cohort studies, and RCTs throughout 2023–2025[155][159][154]. For every food above, measurable changes in immune markers or illness rates have been demonstrated in at least one peer-reviewed trial.
Top Immunity Foods for Vitamin C
Easy Immunity-Boosting Meal Plan
Balance and variety are key! Aim to include at least 6–8 of the top 15 foods weekly. Here’s a research-backed, practical meal template:
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with mixed berries + crushed almonds, or eggs + sautéed spinach/peppers + citrus fruit
- Lunch: Salmon or mackerel salad with leafy greens, bell pepper, broccoli, and sunflower seeds
- Dinner: Stir-fry with assorted mushrooms, garlic, ginger, sweet potato, and chicken or tofu
- Snacks: Green tea, dark chocolate square (70%+ cacao), orange slices, mixed nuts, carrot/celery sticks dipped in yogurt
- Immune boost: Elderberry tea or syrup during cold/flu season; Kombucha or kefir for more probiotics; fresh ginger-lemon tea for stress days
Frequently Asked Questions
Are “superfoods” for immunity a real thing?
Yes—systematic reviews from 2023–2025 support that berries, mushrooms, yogurt, fatty fish, and leafy greens provide measurable immune benefits in humans[155][159][154].
How fast will I see immune benefits from these foods?
Some effects (vitamin C, probiotics) may occur in days to one week. Beta-glucans and vitamin D benefits appear over weeks. Consistency is key for long-term gains[155][116].
Can supplements replace immune-boosting foods?
Whole foods provide multiple synergistic nutrients; supplements help fill gaps but do not provide the same antioxidant and fiber matrix[161][160].
What if I have allergies or dietary restrictions?
Many top-15 options are plant-based and gluten-free. Substitute as needed—e.g., seeds for nuts, legumes for yogurt, and algae/supplements for fish.[155][155]
Are organic foods better for immunity?
Both organic and conventionally grown foods supply the same immune-supporting nutrients. Prioritize variety and eating the top foods regularly for maximal benefit[161].
Conclusion & Next Steps
The verdict is in: Superfoods for immunity aren’t hype—they’re clinically proven to work, especially when you eat a wide range, consistently, alongside good sleep, stress management, and movement[161][155][159]. Choose more colors, more plants, healthy fats, and probiotic-rich foods. Your healthy, resilient future starts on your plate—today!
Read More Nutrition Tips

